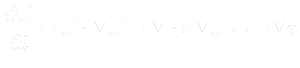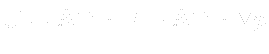Previous: Algorithms PISO and SIMPLE Up: Algorithms PISO and SIMPLE Next: SIMPLE
This is an automatically generated documentation by LaTeX2HTML utility. In case of any issue, please, contact us at info@cfdsupport.com.
PISO
- Assume Navier-Stokes equations for incompressible fluid flow
- Mass conservation equation (continuity equation)
- Momentum conservation equation (velocity equation)
- When discretized momentum conservation equation:
- Matrix linear system:
- Matrix
 is diagonal, with diagonal of original matrix
is diagonal, with diagonal of original matrix 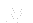
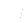 is vector corresponding to (
is vector corresponding to ( )
)- Rewriting (
 ) with substitution from (
) with substitution from ( ):
): - Express
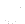 from equation (), i.e. momentum correction equation :
from equation (), i.e. momentum correction equation :
- We combine momentum correction equation (
 ) and continuity equation (
) and continuity equation ( ), which gives us:
), which gives us: - PISO algorithm description:
- Computation starts, initial
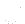 and
and 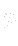 are chosen
are chosen - Time step starts
- Boundary conditions are updated
- Linear system is solved
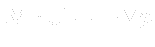
- Obtained new
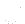
- Building matrix
 and vector
and vector 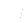
- Mass flow over cell faces is computed
- Pressure correction is applied (
 )
) - Obtained new
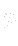
- Mass flow over cell faces is corrected
- Momentum correction is applied (
 )
) - Obtained new corrected
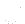
- Boundary conditions are updated
- Steps 6 – 13 are repeated with respect to nCorrectors value
- Time step ends
- PISO algorithm in source code:
- Take a look at solver icoFoam:
# less $FOAM_SOLVERS/incompressible/icoFoam/icoFoam.CInfo<< "\nStarting time loop\n" << endl;
- At the beginning of the computation the output is : Starting time loop
while (runTime.loop()) { Info<< "Time = " << runTime.timeName() << nl << endl; #include "readPISOControls.H" #include "CourantNo.H" - Cycle over all time steps
- Actual time layer is written on the output
- Include header files
fvVectorMatrix UEqn ( fvm::ddt(U) + fvm::div(phi, U) - fvm::laplacian(nu, U) ); - Momentum matrix
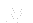 is created (UEqn)
is created (UEqn) - UEqn is the left hand side of equation (
 )
)solve(UEqn == -fvc::grad(p));
- Solves system
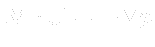
// --- PISO loop for (int corr=0; corr<nCorr; corr++) { - Start of PISO algorithm
- Loop runs until the repetition reaches the value nCorrectors
volScalarField rAU(1.0/UEqn.A());
- The matrix
 is saved as rAU
is saved as rAUvolVectorField HbyA(constrainHbyA(rAU*UEqn.H(), U, p));
- Evaluates relation
 and saves to Hbya
and saves to HbyasurfaceScalarField phiHbyA ( "phiHbyA", fvc::flux(HbyA) + fvc::interpolate(rAU)*fvc::ddtCorr(U, phi) ); adjustPhi(phiHbyA, U, p); // Update the pressure BCs to ensure flux consistency constrainPressure(p, U, phiHbyA, rAU); // Non-orthogonal pressure corrector loop while (piso.correctNonOrthogonal()) { // Pressure corrector fvScalarMatrix pEqn ( fvm::laplacian(rAU, p) == fvc::div(phiHbyA) ); pEqn.setReference(pRefCell, pRefValue); pEqn.solve(mesh.solver(p.select(piso.finalInnerIter()))); - Pressure correction loop solves equation

if (piso.finalNonOrthogonalIter()) { phi = phiHbyA - pEqn.flux(); } } - Momentum correction
#include "continuityErrs.H"
- Including header file for continuity error evaluation
U = HbyA - rAU*fvc::grad(p); U.correctBoundaryConditions(); } - Momentum (velocity) correction
- Boundary conditions correction
- End of current time step
runTime.write();
- Writes data to disk (if it is in the time layer where it is told to write down)
Info<< "ExecutionTime = " << runTime.elapsedCpuTime() << " s" << " ClockTime = " << runTime.elapsedClockTime() << " s" << nl << endl; } Info<< "End\n" << endl; - Writes time information
- End of computation
Previous: Algorithms PISO and SIMPLE Up: Algorithms PISO and SIMPLE Next: SIMPLE