Next: Model setting without an Up: Alternative formulation Previous: Alternative formulation Contents Index
Running snappyHexMesh - Rotor Region
Utility snappyHexMesh refines background mesh in direction to the surface model, reading set-up from system/snappyHexMeshDict:
// Which of the steps to run
castellatedMesh true;
snap true;
addLayers true;
// Geometry. Definition of all surfaces. All surfaces are of class
// searchableSurface.
// Surfaces are used
// - to specify refinement for any mesh cell intersecting it
// - to specify refinement for any mesh cell inside/outside/near
// - to 'snap' the mesh boundary to the surface
geometry
{
align-rot-guide.stl { type triSurfaceMesh; name rotor_spiral_interface; }
shroud-rot.stl { type triSurfaceMesh; name shroud_rot_wall; }
hub-rot.stl { type triSurfaceMesh; name hub_rot_wall; }
blade-rot.stl { type triSurfaceMesh; name blade_rot_wall; }
align-rot-draft.stl { type triSurfaceMesh; name rotor_drafttube_interface; }
};
// Settings for the castellatedMesh generation.
castellatedMeshControls
{
// Refinement parameters
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// If local number of cells is >= maxLocalCells on any processor
// switches from from refinement followed by balancing
// (current method) to (weighted) balancing before refinement.
maxLocalCells 100000;
// Overall cell limit (approximately). Refinement will stop immediately
// upon reaching this number so a refinement level might not complete.
// Note that this is the number of cells before removing the part which
// is not 'visible' from the keepPoint. The final number of cells might
// actually be a lot less.
maxGlobalCells 2000000;
// The surface refinement loop might spend lots of iterations refining just a
// few cells. This setting will cause refinement to stop if <= minimumRefine
// are selected for refinement. Note: it will at least do one iteration
// (unless the number of cells to refine is 0)
minRefinementCells 0;
// Allow a certain level of imbalance during refining
// (since balancing is quite expensive)
// Expressed as fraction of perfect balance (= overall number of cells /
// nProcs). 0=balance always.
maxLoadUnbalance 0.10;
// Number of buffer layers between different levels.
// 1 means normal 2:1 refinement restriction, larger means slower
// refinement.
nCellsBetweenLevels 2;
// Explicit feature edge refinement
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// Specifies a level for any cell intersected by explicitly provided
// edges.
// This is a featureEdgeMesh, read from constant/triSurface for now.
// Specify 'levels' in the same way as the 'distance' mode in the
// refinementRegions (see below). The old specification
// level 2;
// is equivalent to
// levels ((0 2));
features
(
//{
// file "someLine.eMesh";
// //level 2;
// levels ((0.0 2) (1.0 3));
//}
);
// Surface based refinement
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// Specifies two levels for every surface. The first is the minimum level,
// every cell intersecting a surface gets refined up to the minimum level.
// The second level is the maximum level. Cells that 'see' multiple
// intersections where the intersections make an
// angle > resolveFeatureAngle get refined up to the maximum level.
refinementSurfaces
{
// patches
shroud_rot_wall { level (4 5); patchInfo { type wall; } }
hub_rot_wall { level (4 5); patchInfo { type wall; } }
blade_rot_wall { level (5 5); patchInfo { type wall; } }
// rotor boundaries
rotor_spiral_interface { level (3 4); patchInfo { type patch; } }
rotor_drafttube_interface { level (3 4); patchInfo { type patch; } }
}
// Feature angle:
// - used if min and max refinement level of a surface differ
// - used if feature snapping (see snapControls below) is used
resolveFeatureAngle 30;
// Region-wise refinement
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// Specifies refinement level for cells in relation to a surface. One of
// three modes
// - distance. 'levels' specifies per distance to the surface the
// wanted refinement level. The distances need to be specified in
// increasing order.
// - inside. 'levels' is only one entry and only the level is used. All
// cells inside the surface get refined up to the level. The surface
// needs to be closed for this to be possible.
// - outside. Same but cells outside.
refinementRegions
{
//box1x1x1
//{
// mode inside;
// levels ((1.0 4));
//}
//sphere.stl
//{
// mode distance;
// levels ((1.0 5) (2.0 3));
//}
}
// Mesh selection
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// After refinement patches get added for all refinementSurfaces and
// all cells intersecting the surfaces get put into these patches. The
// section reachable from the locationInMesh is kept.
// NOTE: This point should never be on a face, always inside a cell, even
// after refinement.
locationInMesh (1.001 0 -1.001);
// Whether any faceZones (as specified in the refinementSurfaces)
// are only on the boundary of corresponding cellZones or also allow
// free-standing zone faces. Not used if there are no faceZones.
allowFreeStandingZoneFaces true;
}
- Lines 28-35 define the geometry using *.stl files of triSurfaceMesh type. The parameter nameassign a name to the given part of geometry.
- Lines 105-115 define a level of surface refinements and type of new patches.
Create the mesh running snappyHexMesh utility:
# snappyHexMesh
When finished, check the mesh running checkMesh and view the mesh in paraview:
# checkMesh -latestTime
# paraFoam
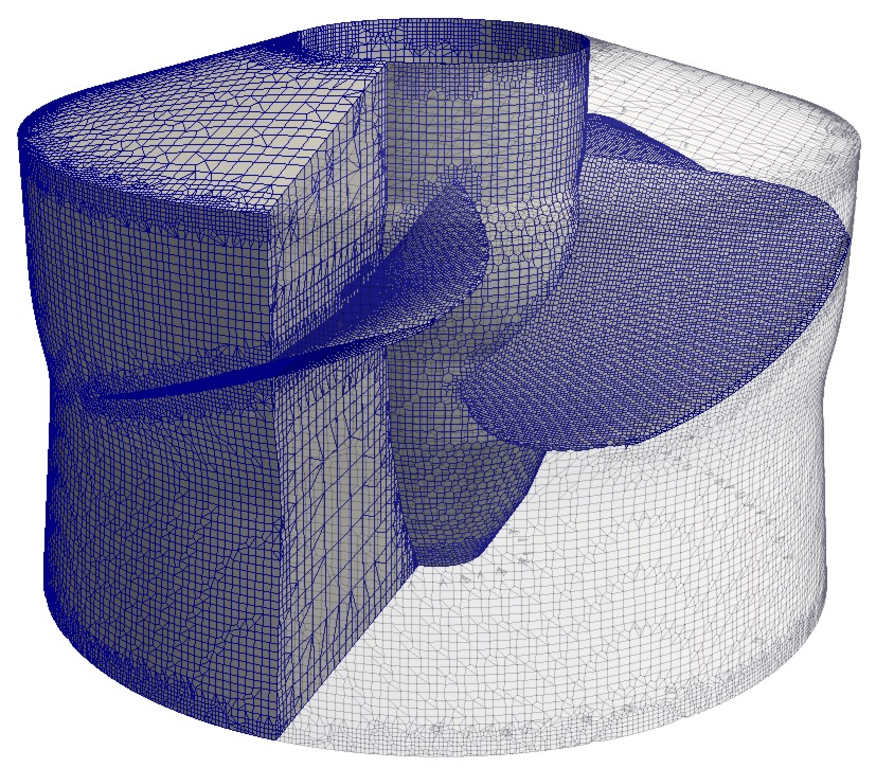
Figure: Kaplan turbine rotor region mesh view.
The final mesh is located in directory with the highest number.